Industrial Display & Embedded Computing Glossary
ARM Processor: A low-power CPU architecture used in embedded systems and industrial panel PCs for efficient performance.
Active Matrix: Technology using thin film transistors for fast response and high-quality LCD performance.
Adaptive Brightness: Automatic adjustment of screen luminance based on ambient light conditions.
Aluminium Chassis: Durable metal housing providing strength and heat dissipation for industrial devices.
Anti-Glare Coating: Surface treatment reducing reflections and improving visibility in bright conditions.
Anti-Reflective Glass: Glass treatment that minimizes light reflection and enhances display readability.
Aspect Ratio: The ratio of a display’s width to its height, important for defining screen format such as 16:9 or 4:3.
Auto-Dimming: Feature allowing displays to adjust brightness automatically for comfort and efficiency.
BIOS: Basic Input/Output System controlling hardware startup and configuration in embedded PCs.
Backlight: The illumination source behind an LCD panel, often LED-based, controlling display brightness and visibility.
Bar Type Display: A wide-format display designed for signage, transport, and industrial applications requiring panoramic visuals.
Bezel: The frame surrounding a display screen, available in various designs including narrow and open-frame types.
Bonded Touch: Touchscreen integrated with display glass for improved durability and visual performance.
Boot Time: The time taken by an embedded system to initialize and load the operating environment.
Brightness (nits): Measurement of a display’s luminance; industrial screens often exceed 1000 nits for outdoor readability.
Brightness Control: Adjustment mechanism for screen luminance via hardware or software.
Bus Interface: Connection pathway enabling communication between computer components and peripherals.
CAN Bus: A robust communication protocol used in industrial systems for real-time control between devices.
CPU: Central Processing Unit — the main processor executing tasks and instructions within embedded computers.
Cables & Connectors: Physical interfaces that transmit power or data between system components.
Capacitive Touch: Touch technology using electrical sensing, enabling multitouch and glove operation on modern touchscreens.
Chassis Ground: Safety grounding system to prevent electrical interference and static buildup.
Cloning Function: Ability to duplicate display output across multiple monitors simultaneously.
Color Gamut: Range of colors a display can reproduce, crucial for image accuracy.
Compact Design: Hardware layout optimized for limited spaces or embedded integrations.
CompactFlash: A form of removable storage used in older embedded systems for data logging and OS storage.
Contrast Ratio: The ratio between the brightest and darkest points a display can show, affecting image clarity.
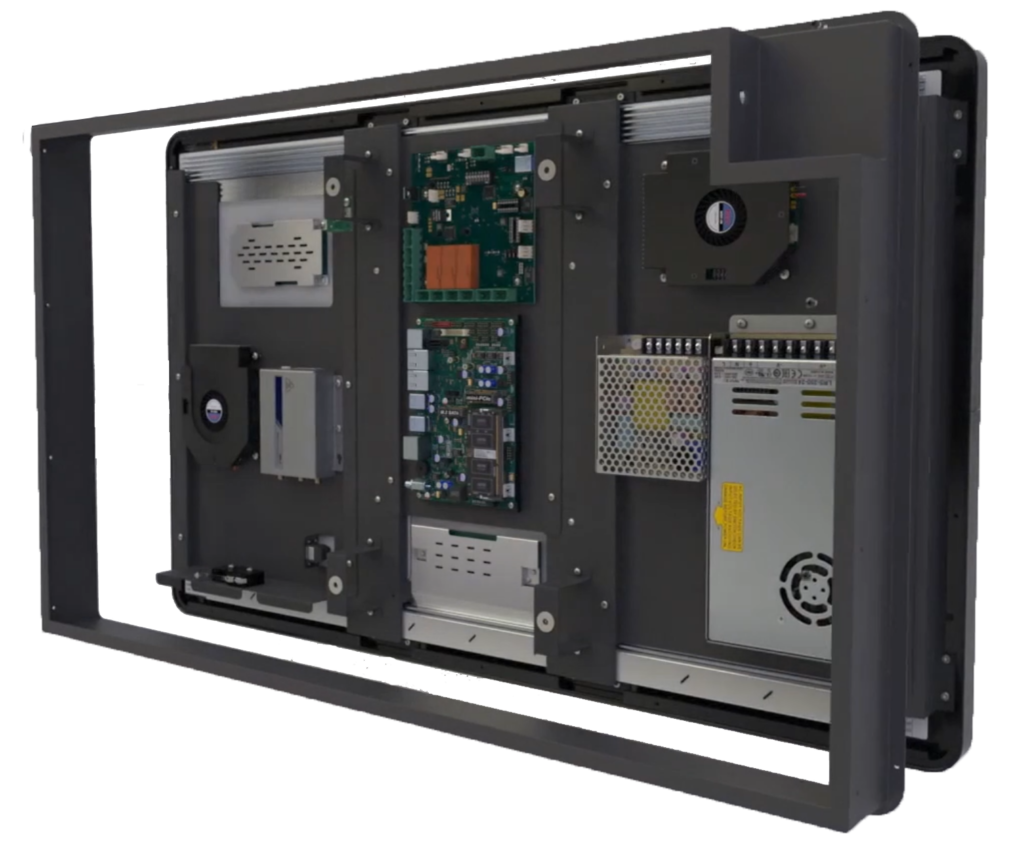
Controller Board: Electronics managing display input signals such as HDMI, VGA, or DisplayPort to drive LCD panels.
Cooling Fan: Mechanical device that dissipates heat to maintain safe operating temperatures.
Custom Firmware: Specialized low-level software tailored for specific industrial applications.
DC Input: Direct current power input used in industrial monitors and PCs, ensuring stable operation in harsh environments.
DC-DC Converter: Electronics module converting one DC voltage level to another efficiently.
DIN Rail Mounting: Common industrial mounting system for control cabinets and automation equipment.
DVI: Digital Visual Interface — a video connection standard found in many industrial display controllers.
Data Logging: Recording system events or measurements for analysis and traceability.
Display Calibration: Process of adjusting colour, brightness, and contrast to maintain accuracy.
Display Glass: Protective cover that safeguards the LCD panel and enhances aesthetics.
DisplayPort: A digital interface transmitting audio and video signals between computers and monitors.
Dustproof Design: Engineering approach ensuring protection from airborne particles and debris.
EMC Compliance: Certification ensuring devices do not emit or suffer from electromagnetic interference.
ESD Protection: Electrostatic discharge shielding to protect sensitive electronic components.
Edge-to-Edge Glass: A design feature offering a seamless front surface ideal for hygiene-critical or aesthetic applications.
Embedded Computer: A self-contained computing unit integrated into equipment for automation and control tasks.
Embedded GPU: Graphics processor integrated into CPUs or chipsets for visual rendering.
Embedded OS: Operating systems such as Windows IoT or Linux, optimized for industrial embedded platforms.
Expansion Slot: Hardware interface allowing installation of additional cards or modules.
Fan Filter: Mesh filter preventing dust accumulation in cooling fans or vents.
Industrial Automation: Use of control systems such as PLCs and PCs to manage machinery and processes.
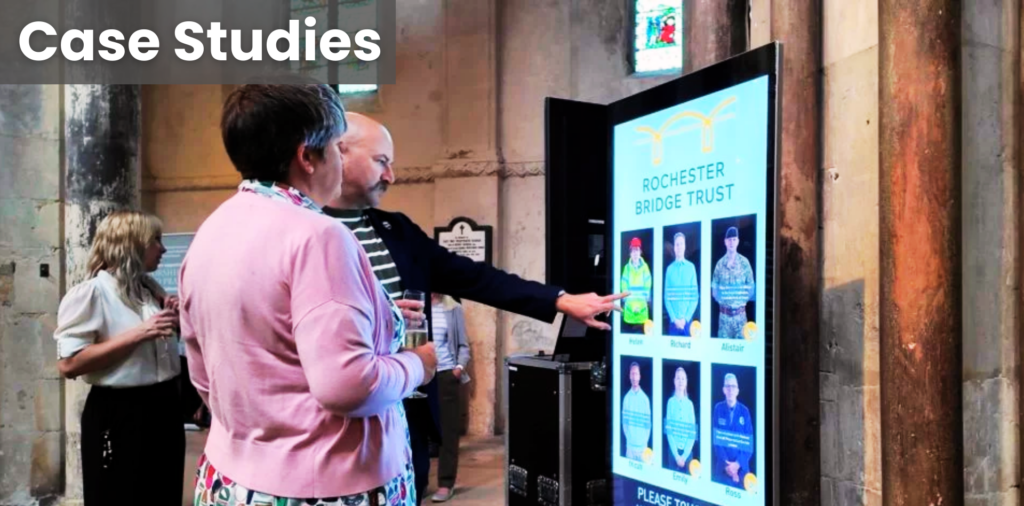
Industrial Display: A rugged screen designed to perform reliably in harsh or demanding environments.
Industrial Grade: Specifically engineered for durability, reliability, and extended operation.
Industrial Motherboard: Main circuit board optimized for industrial reliability and lifespan.
Industrial Panel PC: A robust computer integrating display and processing components for industrial automation control.
Infrared Touch: Touch technology using light beams across the screen for input detection.
Ingress Protection (IP Rating): Standard defining resistance to dust and water, e.g., IP65 or IP69K for sealed systems.
Input Voltage Range: Accepted voltage levels for safe and stable operation of a device.
Interface Board: Circuit board connecting input signals to the LCD, managing formats like LVDS or eDP.
IoT Gateway: Device connecting industrial machines to the Internet of Things for data exchange.
Isolation Circuit: Electrical design preventing interference or damage between components.
LCD: Liquid Crystal Display — widely used flat-panel technology in industrial and consumer monitors.
LED Backlight: Energy-efficient lighting behind LCDs providing uniform brightness and colour stability.
LED Indicator: Small light showing system status or operational activity.
LVDS: Low-Voltage Differential Signaling — a data transmission method used between controller and display panel.
Linux: Open-source operating system frequently used in embedded applications.
Long Lifetime: Refers to displays and components designed for 24/7 industrial use and long-term availability.
MIPI DSI: Mobile Industry Processor Interface — a compact display connection standard for embedded designs.
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF): Statistical estimate of product reliability and lifespan.
Microcontroller: Compact processor used for dedicated control tasks in embedded systems.
Mini-ITX: Small motherboard form factor used in compact industrial PCs.
Modbus: Industrial communication protocol for connecting electronic devices.
Mounting Bracket: Hardware accessory used for securely fixing displays to walls or structures.
Multi-Touch: Touch capability that detects and responds to multiple simultaneous touch points.
NEMA Enclosure: Standard defining protection levels for electronic housings in industrial settings.
NVMe: Non-Volatile Memory Express — high-speed interface for SSD storage devices.
OEM Customization: Tailoring of products for specific clients under their brand or specification.
OSD Lockout: Feature preventing unauthorized adjustment of display settings.
On-Screen Display (OSD): Menu system allowing display parameter adjustments via software interface.
Open Frame Monitor: Display supplied without housing for integration into custom enclosures or kiosks.
Operating Temperature: Temperature range within which a device performs reliably.
Optical Bonding: Process of adhering protective glass to LCD to improve clarity and shock resistance.
Optical Clarity: Measure of transparency and visibility through protective display glass.
P-CAP: Projected Capacitive Touch — advanced touch technology offering durability and multi-touch functionality.
PCB: Printed Circuit Board hosting electronic components and signal routing.
PWM Dimming: Pulse Width Modulation technique controlling backlight brightness efficiently.
Panel Brightness: Overall luminance capability of a display panel.
Panel Mount: Installation method where the monitor is fixed from the front into a flat surface or panel.
Panel PC: A compact all-in-one computer integrating a touchscreen and embedded motherboard.
Passive Cooling: Thermal management method using natural convection instead of fans.
Pixel Pitch: Distance between adjacent pixels, determining image sharpness.
PoE: Power over Ethernet — allows devices to receive power and data through one cable.
Power Supply Unit: Hardware converting and distributing electrical power to components.
Projected Capacitive: Touch technology with transparent electrodes enabling multi-touch detection.
Protective Coating: Layer applied to surfaces for chemical or physical protection.
RAM: Random Access Memory used by embedded computers for processing data.
RS232: Serial communication standard used for data exchange between control systems and displays.
RS485: Differential serial communication interface supporting longer distances in industrial automation.
Resolution: Number of pixels displayed horizontally and vertically defining image detail.
Rugged Design: Products built to withstand vibration, temperature extremes, and shock for industrial environments.
Rugged Enclosure: Durable housing protecting internal components from impact and vibration.
SATA: Serial ATA — interface connecting storage devices like SSDs to embedded computers.
SSD: Solid-State Drive — high-speed, reliable storage used in embedded and industrial PCs.
Serial Port: Legacy interface used for industrial communication and configuration.
Shock Resistance: Ability to withstand mechanical impact without damage or malfunction.
Smart Display: Integrated display combining interactive and networked computing features.
Solid State: Technology with no moving parts, enhancing reliability and longevity.
Stainless Steel Panel PC: Corrosion-resistant embedded system ideal for food and pharmaceutical environments.
Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW): Touch technology using ultrasonic waves on a glass surface for input detection.
System-on-Chip (SoC): Integrated circuit combining CPU, GPU, and memory for compact efficiency.
TFT: Thin Film Transistor — active matrix technology enhancing image sharpness and response time.
Thermal Management: Control of heat dissipation to maintain system reliability.
Touch Calibration: Adjustment ensuring accurate alignment between touch input and display coordinates.
Touch Controller: Electronics converting physical touch input into digital coordinates for system processing.
Touch Glass: Protective layer that allows user interaction and shields the display underneath.
Touch Sensitivity: Responsiveness level of a touchscreen to user input.
Touchscreen Controller: Interface converting touch input into coordinate data for system processing.
USB: Universal Serial Bus — standard interface for peripherals and communication between devices.
USB-C: Reversible USB connector supporting power, data, and video transmission.
UV Protection: Coating or material preventing UV degradation of display components.
VESA Mount: Standardized mounting pattern for attaching monitors to arms, walls, or brackets.
VGA: Analog video interface still common in legacy industrial systems.
Viewing Angle: Maximum angle from which a display can be viewed without image distortion.
Voltage Regulation: Maintaining consistent power supply for system stability.
Watchdog Timer: Safety mechanism that resets the system in case of malfunction.
Waterproof Connector: Sealed interface preventing ingress of moisture and contaminants.
Wide Temperature Range: Capability of operating in extreme hot or cold environments, crucial for outdoor applications.
Wide Viewing Angle: Display feature allowing visibility from various directions without colour shift.
Windows IoT: Microsoft operating system optimized for embedded and industrial computing devices.
Wireless Connectivity: Capability to connect via Wi-Fi or Bluetooth without physical cabling.
X86 Architecture: Processor instruction set widely used in industrial and embedded PCs.
Zero Bezel Design: Touchscreen layout with seamless front surface for easy cleaning and modern aesthetics.
eDP: Embedded DisplayPort — high-speed digital interface used between CPU and LCD panel.
Need More Information?
CALL US +44 (0)1634 791600