+44 (0)1634 791600
info@crystal-display.com
Newsletter Sign Up!
+44 (0)1634 791600
info@crystal-display.com




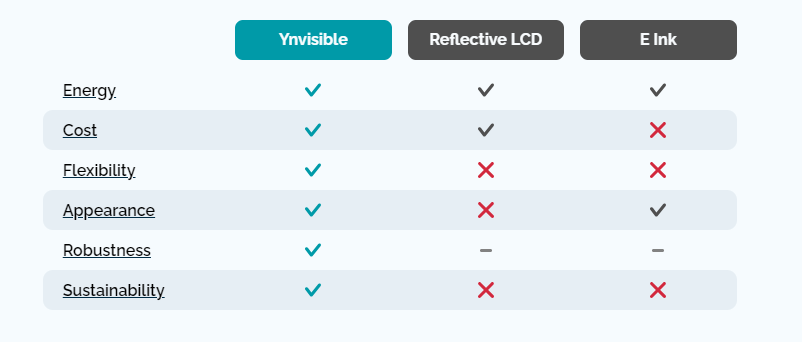
Ynvisble Printed e-paper displays utilize electrochromic reflective technology, offering excellent visibility with very low angle dependency. These displays are ultra-low power, characterized by semi-bistability. This means that power is primarily consumed during display transitions, with only occasional refresh pulses required, typically occurring once every 5 minutes.

A printed e-paper display, also known as a printed electronic paper display or simply e-paper display, is a type of electronic display technology that mimics the appearance of ink on paper. It utilizes electronic ink (e-ink) or similar materials to create text that is highly readable and can be updated electronically.
Using an ultra-low power consumption display that’s easy to integrate with minimal or no additional driver electronics reduces system-level costs. Many clients have been able to cut back or eliminate their existing power supply by opting for our segmented displays.
Ynvisible seldom creates standard display components. We believe each product deserves a unique display for the best user experience. The printability of our displays ensures a level of customization not available with other display technologies, resulting in an attractive appearance highly valued by both product designers and end-users.
Display segments can be designed in essentially any shape and form. Letters, symbols, numbers, and graphics elements are all possible.
Colour filters and other static graphic elements can easily be printed on top of the display. The graphic overlay is commonly used to add graphics that should always be visible and complement the dynamic display segments.
Most conventional displays are bulky rectangle shapes. This is not the case for Ynvisible Displays. Essentially any cut-out shape is possible, whatever fits your product the best.
These displays boast a wide operating range and are highly resistant to heat and cold shocks. Thanks to their plastic substrate, they are exceptionally durable when it comes to physical impacts, bending, and piercing. Unlike conventional glass-based displays, they won’t break, crack, or shatter.
Ynvisible’s displays are eco-friendly and non-toxic, benefiting from energy-efficient production processes, organic materials, and minimal material usage. They are an ideal choice for single-use and disposable products.
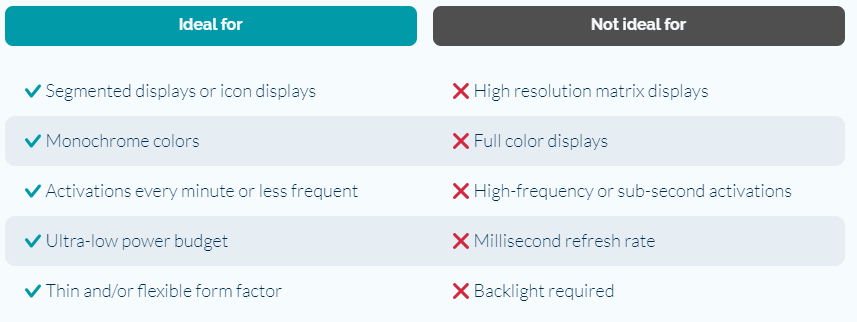
The Ynvisible Display is an e-paper technology, a so-called Electrochromic Display (“ECD”), based on organic electrochromic polymers. It is categorized as a reflective display – meaning that it reflects ambient light instead of using a backlight. The displays are screen-printed on a plastic substrate, which makes the displays very thin and flexible.
Ynvisible’s e paper displays boast the lowest energy consumption on the market for most applications. In static use (when maintaining the same image), the display consumes up to 0.28µW per cm² segment area. For dynamic use, power consumption varies with the number of display updates per day, based on the formula below.
P = 1,67 + 0,01 × n µW/cm2
n is the number of full display updates per day
Ynvisible leads the industry in Sheet-to-Sheet and Roll-to-Roll production of electrochromic technology. These high-volume production methods, paired with cost-effective material sourcing, significantly reduce the cost of individual displays while ensuring high production yield, fast throughput speed, and premium quality. Opting for Ynvisible’s display technology will lower costs at both the component and system levels.

We’ve moved past the era of unattractive segmented LCDs and LEDs. Now is the time to explore visually captivating alternatives. Let’s experiment with diverse shapes, forms, and colours—all while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Entering the nanowatt power era—ideal for battery-driven or battery-less IoT devices that demand ultra-low power consumption. This breakthrough technology opens doors to efficient and sustainable solutions for a wide range of applications in the Internet Of Things (IOT), enabling longer battery life and environmental friendliness.

Opting for our Ynvisible e-paper displays not only lowers costs at the component and system levels but also enables ultra-low-cost mass production through efficient roll-to-roll screen-printing processes. This approach offers significant savings while maintaining high-quality performance.
Electrochromic displays are created using screen-printable electrochromic polymers. “Electrochromism” describes the effect in which a material changes color in response to an electrical signal. To produce these displays, thin layers of electrochromic materials and high-performance electrolytes are printed into a flexible “electrochromic stack.” When voltage is applied, the electrochromic material, in the presence of the electrolyte, undergoes chemical oxidation and reduction, resulting in a tunable color change. These displays are exceptionally thin, measuring just 200 µm, and are flexible enough to wrap around a pencil.
Printed electrochromic displays offer wide-ranging applications, from luxury goods to disposable devices, thanks to their design flexibility, adaptable form factors, and broad usability. Common uses include medical devices, smart packaging and containers, logistics and cold chain monitoring, consumer electronics, smart cards, wearable tech and patches, as well as fast-moving consumer goods.
The top 5 reasons why our clients choose printed displays are:
No, printed displays and E-Ink displays are fundamentally different technologies. While both are reflective displays—meaning they rely on ambient light and don’t require backlighting—the underlying mechanisms differ. E-Ink uses electrophoretic technology, whereas our displays are based on organic electrochromic materials.
The refresh or update speed of the display depends on the segment size, with larger segments updating more slowly than smaller ones. Activating a 4 mm² display segment using a 3V drive protocol typically takes about 200 milliseconds.
The contrast ratio is typically ≥ 1:3. Ynvisible’s displays resemble printed graphics more than traditional electronic displays, making Color Difference (ΔE) a more fitting measure to express the visual change between the display segment’s off (neutral) and on (activated) states. The Color Difference value varies based on the display color; however, for our most common Gray-to-Blue display, the typical ΔE is 30.
Our displays offer the lowest power consumption on the market for most applications. In static mode (when the display image remains unchanged), power usage is capped at 0.28 µW per cm² of segment area. For dynamic usage, power consumption varies with the number of daily updates, calculated as:
P=0.28+0.01×n μW/cm2P = 0.28 + 0.01 \times n \, \mu W/cm^2P=0.28+0.01×nμW/cm2
where n represents the number of full display updates per day. Activating one square centimeter of display area requires approximately 1 mJ.
Our displays are available in a variety of colors, though they are monochrome, as each color must be predefined. While full-color displays like RGB or CMY are not possible, multiple colors can be incorporated side by side within the same display. We offer a broad selection of colors and can customize tones to match your brand. Our standard colors include Gray, Red, Green, Magenta, and Yellow, with Gray providing the highest readability.
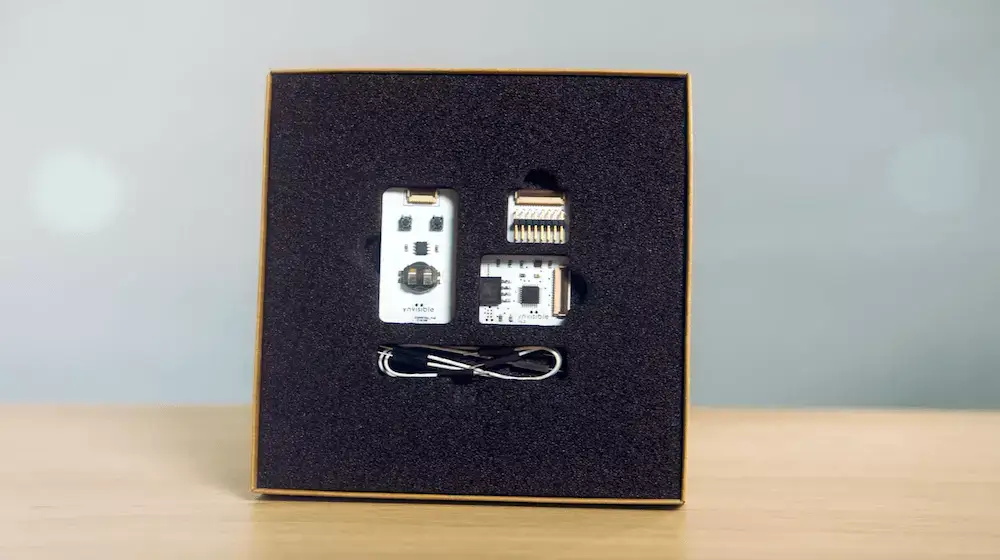

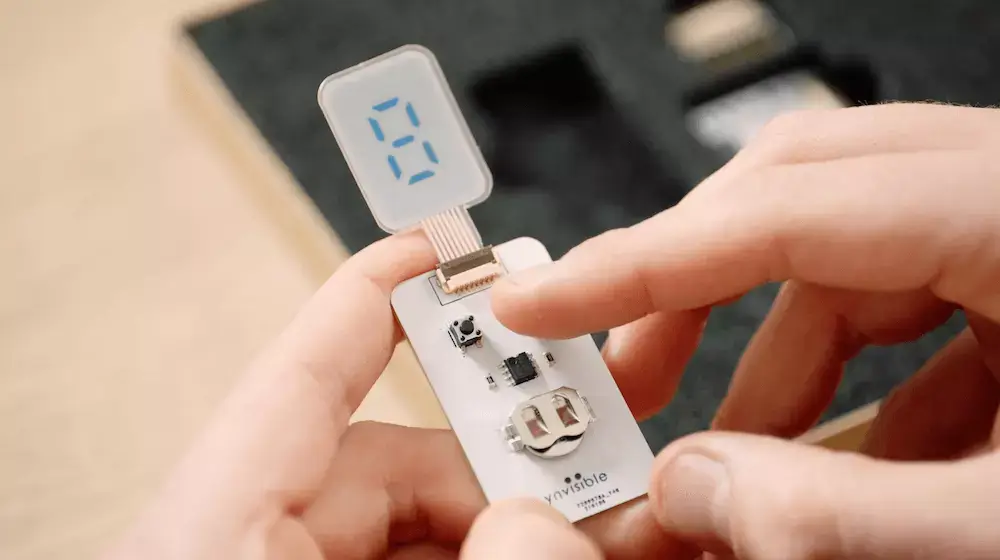
The E-Paper Display Kit is the ideal way to get started with our technology. Try it today!
Assess the capabilities of the ultra-low-power, thin, and flexible printed e-paper displays. Each e-paper display kit includes various display designs, a manual display driver, and an e-paper display driver equipped with an I2C interface.

Medical
Measurement
Security
Agriculture
Security
Consumer goods
Retail
Wearables
This is a 100% Customised product designed for volume production, to deliver the best price advantages
The product is Semi -Bistable, a battery is required to pulse the display however extremely low power and huge cost advantages (Energy calculation can be found below)
Printed E-paper Displays are Segmented only, no option for graphical.
Price advantage becomes more advantageous with display size increase.
NRE required for soft tooling (Sheet to Sheet 500+) and Hard tooling (Roll-Roll) for 500K+pcs, however very cost effective comparable to alternative technologies.
Fundamentally the displays are very straightforward to drive. A positive voltage (in reference to the counter electrode) turns ON the display segment, while a negative voltage (or shortening the work and counter electrode) turns OFF the segment. A higher voltage level enables a faster switching speed, while a lower voltage enables a longer lifetime. Typically, a good trade-off between lifetime and switch speed is to use ±1,5V across the segment. However, the displays achieve full contrast down to 1V.
If switching speed is not an issue, it is recommended to keep the voltage to a minimum. Higher voltage is optional for devices with shorter lifetime requirements. Turn OFF voltage should typically be kept the same as turn ON voltage (but with the opposite polarity) but if a longer switching time is acceptable, it is possible to shorten (≈0V) the counter electrode and the work electrode to turn the segment OFF (Driving scheme E). Below follows a few different driving schemes suggestions.
