The Dawn of Edge Computing: Redefining the Future of Data Processing
The Future of Data Processing
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, one concept has been gaining momentum and transforming the way we handle data – Edge Computing. This groundbreaking paradigm shift is redefining the future of data processing, promising faster speeds, reduced latency, and increased efficiency. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of edge computing, exploring its key principles, benefits, and its profound impact on various industries.

What is Edge Computing?
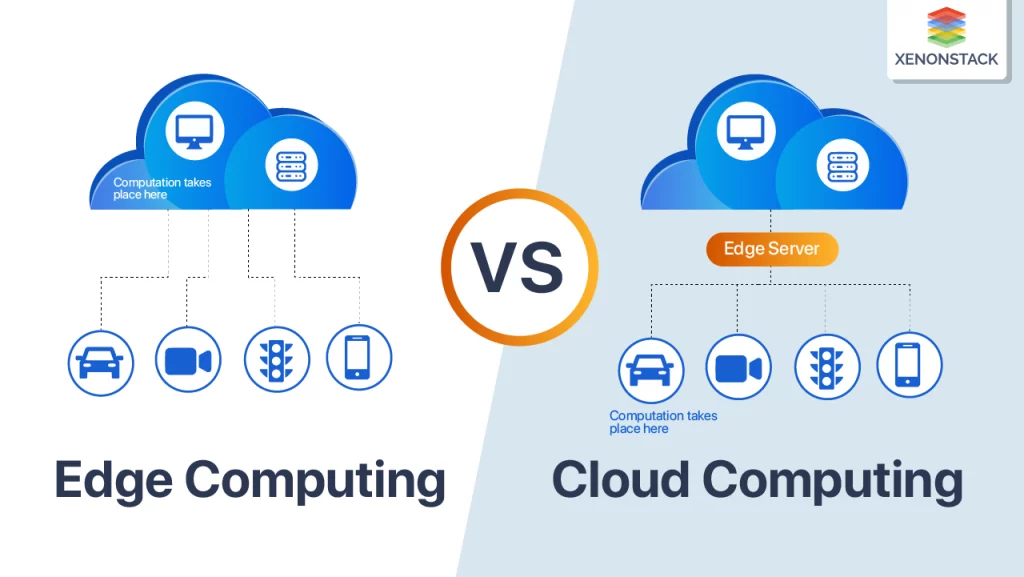
Edge computing is a distributed computing model that brings data processing closer to the source of data generation. Unlike traditional cloud computing, where data is sent to centralized data centers for processing, edge computing pushes data processing to the “edge” of the network, closer to the devices and sensors that collect data.
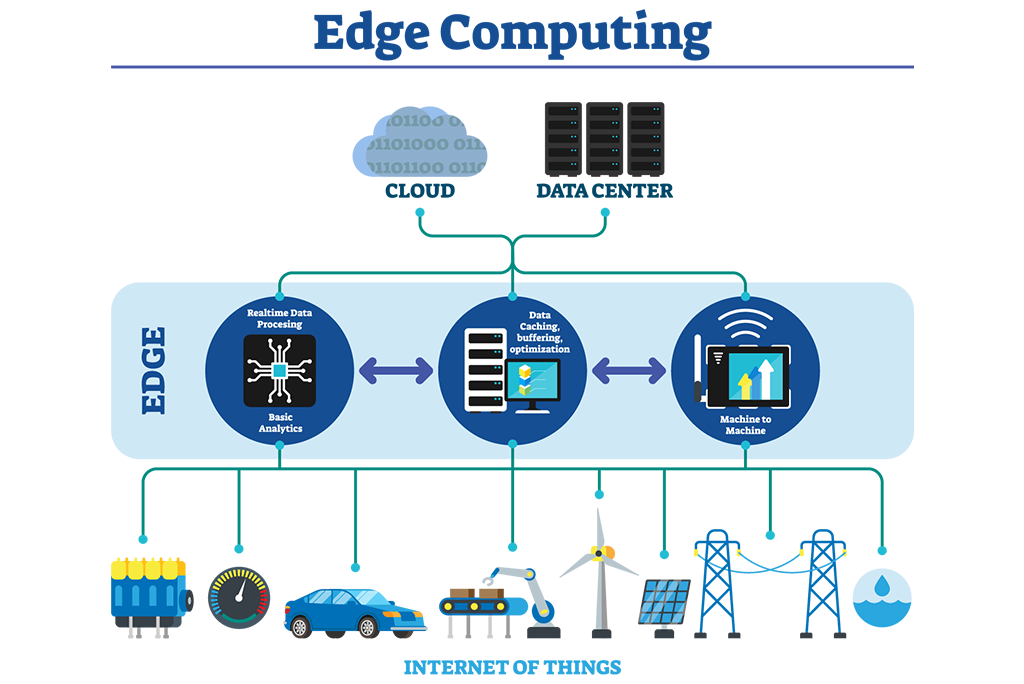
At the core of edge computing are miniature data centers, often referred to as “edge nodes” or “edge servers.” These nodes are strategically placed near the data sources and perform real-time data analysis and processing. This proximity to data sources significantly reduces latency and bandwidth usage, enabling faster response times and improved overall performance.
The Key Principles of Edge Computing
First and foremost, let’s explore the key principles that underpin edge computing:
Proximity: As mentioned earlier, edge computing is all about proximity to data sources. By reducing the physical distance between data processing and data generation, it minimizes the delays caused by transmitting data to distant cloud servers. Consequently, data processing becomes swift and efficient.
Real-time Processing: Edge computing emphasizes real-time data processing. This is crucial for applications where split-second decision-making is critical, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and augmented reality. In these scenarios, real-time processing is not a luxury but a necessity.
Bandwidth Efficiency: By processing data locally, edge computing reduces the burden on network bandwidth. This is particularly important in remote or low-bandwidth environments, ensuring efficient data transfer. Consequently, organizations can make the most of their available network resources.
Data Security and Privacy: Edge computing enhances data security and privacy by keeping sensitive information closer to its source. This reduces the risk of data breaches during data transmission to remote servers. As data breaches continue to pose significant threats, this principle is paramount.
The Benefits of Edge Computing
Now that we’ve explored its principles, let’s delve into the myriad benefits of edge computing:
1. Reduced Latency
One of the most significant advantages of edge computing is its ability to minimize latency. This is crucial for applications like online gaming, autonomous vehicles, and telemedicine, where even milliseconds of delay can have a significant impact on user experience and safety. In essence, latency becomes virtually imperceptible.
2. Enhanced Reliability
Edge computing systems are designed for redundancy and fault tolerance. In case one edge node fails, another can take over seamlessly. This ensures high availability and reliability, making it suitable for mission-critical applications. In essence, reliability is guaranteed.
3. Cost Efficiency
Edge computing can reduce the costs associated with data transfer and storage in the cloud. By processing data locally, organizations can optimize their use of cloud resources and save on bandwidth costs. Consequently, cost-efficiency becomes a reality.
4. Scalability
Edge computing is highly scalable. Organizations can add more edge nodes as needed to handle increased data loads, making it adaptable to changing business requirements. As businesses evolve and grow, scalability remains effortless.
Edge Computing in Various Industries
Edge computing is not limited to a specific industry; it has applications across various sectors:
Manufacturing: In smart factories, edge computing enables real-time monitoring and control of machines, improving efficiency and reducing downtime. Consequently, productivity soars.
Healthcare: Edge computing is used in telemedicine for real-time patient monitoring and diagnosis, especially in remote areas with limited internet connectivity. Consequently, healthcare becomes accessible and efficient.
Retail: In retail, edge computing can be applied to inventory management, enabling real-time tracking of stock levels and reducing out-of-stock situations. Consequently, customer satisfaction soars.
Transportation: Autonomous vehicles rely on edge computing for real-time decision-making, enhancing safety on the roads. Consequently, transportation becomes safer and more efficient.
Agriculture: In precision agriculture, edge computing helps analyze data from sensors and drones to optimize crop management. Consequently, agriculture becomes more sustainable and productive.
Smart Cities: Edge computing is at the heart of smart city initiatives, enabling real-time traffic management, waste management, and energy optimization. Consequently, cities become more sustainable and livable.
In conclusion, edge computing is ushering in a new era of data processing, promising lower latency, enhanced reliability, and cost efficiency. Its application spans across various industries, revolutionizing the way we collect, process, and utilize data. As technology continues to advance, the future undoubtedly belongs to edge computing, redefining our expectations of what’s possible in the digital age. In essence, edge computing is poised to shape our digital future profoundly.
If you would like more information about Edge computing or are interested in any of our products then please get in contact now using the details at the bottom of the page